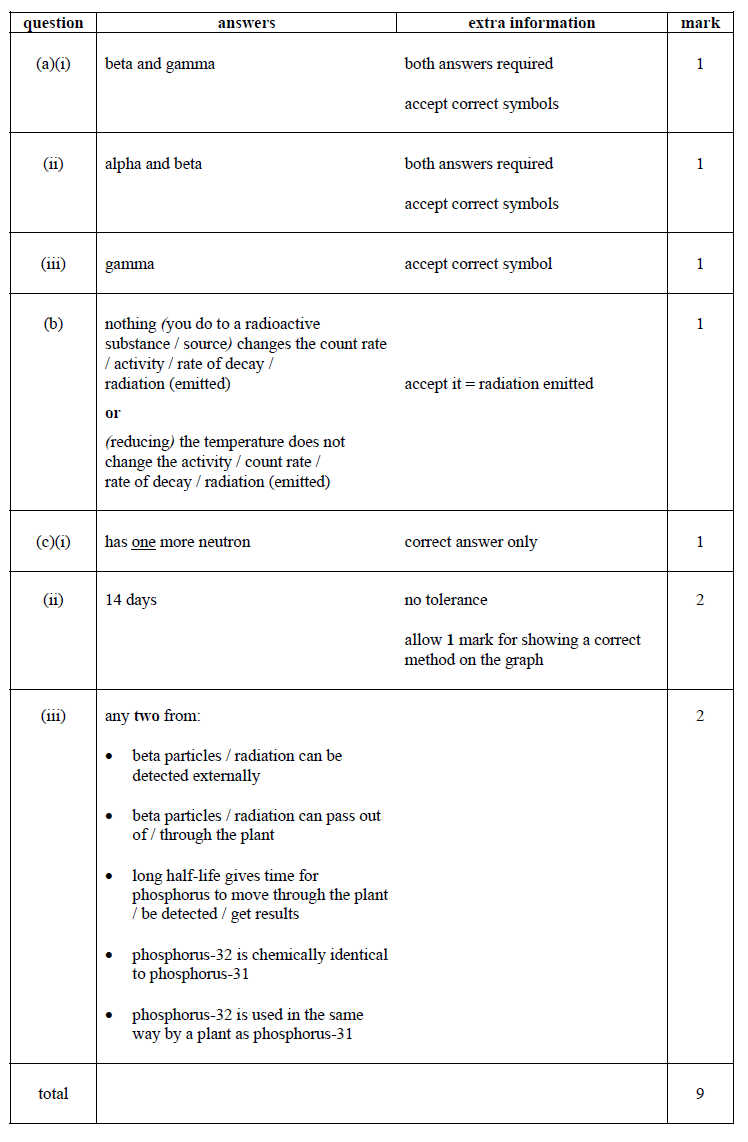
(a) A radioactive source emits alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) radiation.
(i) Which two types of radiation will pass through a sheet of card?
![]()
(1 mark)
(ii) Which two types of radiation would be deflected by an electric field?
![]()
(1 mark)
(iii) Which type of radiation has the greatest range in air?
![]()
(1 mark)
(b) A student suggests that the radioactive source should be stored in a freezer at –20 °C.
The student thinks that this would reduce the radiation emitted from the source.
Suggest why the student is wrong.
(1 mark)
(c) Phosphorus-32 is a radioactive isotope that emits beta radiation.
(i) How is an atom of phosphorus-32 different from an atom of the stable isotope phosphorus-31?
(1 mark)
(ii) The graph shows how the count rate of a sample of phosphorus-32 changes with time.
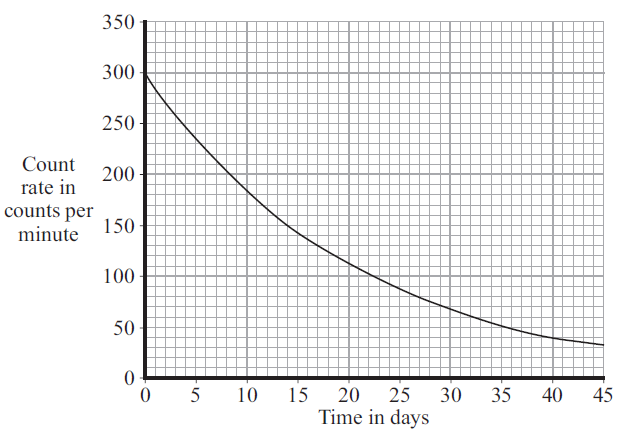
Use the graph to calculate the half-life of phosphorus-32.
Show clearly how you used the graph to obtain your answer.
Half-life = ………………………… days
(2 marks)
(iii) Plants use phosphorus compounds to grow. Watering the root system of a plant with a solution containing a phosphorus-32 compound can help scientists to understand the growth process.

Explain why phosphorus-32 is suitable for use as a tracer in this situation.
 (2 marks)
(2 marks)
How did you do? Click to show the mark scheme
From Q4 P1 AQA January 2008 but now on P2 syllabus
