 –
–
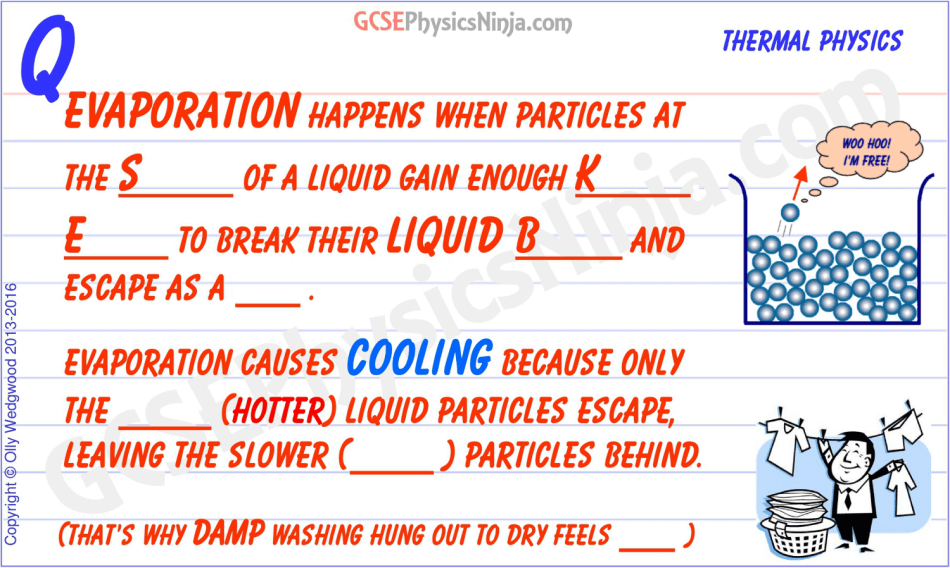
Heat transfer by evaporation
In addition to heat transfer by radiation, conduction and convection, heat can also be transferred by evaporation, and it’s opposite – condensation.
Imagine a whole bunch of liquid particles, moving around and slipping and sliding over each other. Some hotter particles have more kinetic energy than others and therefore move faster.
A few of these might have enough energy to overcome the bonds that keep them in the liquid state. By breaking their liquid bonds, they evaporate becoming a gas. This often happens near the surface of the liquid, but if you heat a liquid to it’s boiling point, particles within the liquid will become a gas, producing the characteristic bubbles that you see when a liquid boils.
When a hotter particle near the surface of the liquid ‘breaks free’ from it’s liquid bonds, it escapes as a gas, carrying away energy from the rest of the liquid. The average energy of the liquid therefore decreases – in other words, the liquid cools down.
This is why evaporation causes cooling – for example:
- You feel cooler when you get out of a swimming pool.
- Damp washing hung out to dry feels cold.
GCSE Physics Keywords: Evaporation, Cooling, Liquid bonds, Kinetic energy, Breaking bonds, Boiling
